Very cool story! Congrats!
08.09.2025 18:13 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

OPEN FACULTY POSITION, INSTITUTE OF MOLECULAR BIOLOGY, ACADEMIA SINICA, TAIWAN - 128 Academia Road, Section 2, Nankang, Taipei, Taiwan job with Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taiwan ...
One tenure-track faculty position is open for a qualified individual to establish an active research program at the IMB.
Be our IMB colleague! Join us for cool science!
[open faculty position at the institute of molecular biology, academia sinica in taiwan]
www.nature.com/naturecareer...
05.09.2025 22:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Thanks Dor!
28.05.2025 16:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Overall, our findings expand our understanding of how bacteria outcompete one another in crowded environments. Check out our story! 💪
27.05.2025 19:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Interestingly, we found that the bacteria secreting Cpe1 are protected from self-poisoning by a protein called Cpi1. Cpi1 blocks the toxin using a unique mode. Unlike many other immunity that block the toxin’s active site, Cpi1 inhibits Cpe1 by blocking the substrate-binding site.
27.05.2025 19:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Using structural and mass spec approaches, we pinpointed the exact cleavage target sequences of Cpe1: in the short “double-glycine” motifs, specifically LHAGGKF, in GyrB and ParE!
27.05.2025 19:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
This interbacterial toxin is called Cpe1. It acts like molecular scissors✂️, cutting the ATPase domains of essential topoisomerases, GyrB and ParE, in competing bacteria. Without the critical proteins, the rival cells can't properly copy their genomes, leading to growth stalls.
27.05.2025 19:57 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Excited to learn that our story on characterizing an interbacterial protease toxin is finally out @plosbiology.org
"An interbacterial cysteine protease toxin inhibits cell growth by targeting type II DNA topoisomerases GyrB and ParE". Led by my wonderful team at Academia Sinica!
27.05.2025 19:57 — 👍 15 🔁 10 💬 2 📌 1
n summary, our findings show that while phage resistance helps bacteria avoid viral infection, it can come at the cost of losing the battle against other bacteria in the environment. A double-edged sword! ⚔️🔬
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
More interestingly, even when Salmonella was treated with an enzyme from phages that degrades LPS, it also became vulnerable to bacterial attacks, demonstrating that phages can indirectly weaken bacteria and affect bacteria-bacteria interaction.
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Further experiments revealed that the O-antigen, a part of the LPS structure, is crucial for protecting Salmonella against these bacterial attacks. Without it, they became easy targets.
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
The reason why Salmonella lose their ability to compete is due to mutations in genes related to their cell membrane, specifically in a structure called LPS (lipopolysaccharide), which normally protects against external stresses. Bacteria with damaged LPS became vulnerable to T6S.
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We used Salmonella phage-resistants as the model for the question. Interestingly, while resistant strains grew and competed normally in liquid media, they struggled when grown on solid media with bacteria with the specialized weapon: type VI secretion system (T6SS)
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Bacteria can become resistant to phages that infect them, but this resistance might weaken their ability to compete with other bacteria. Here, we start by asking how phage-resistant bacteria perform in competition with other competitor bacteria.
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
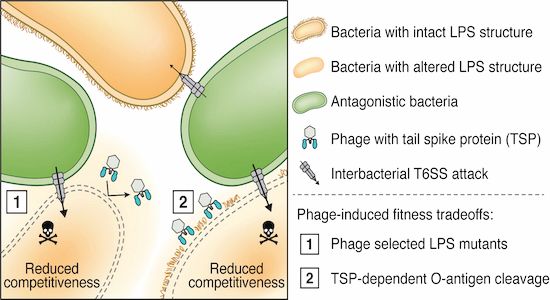
Our Phage infection/T6S story is finally out @embojournal.org! "Surface-mediated bacteriophage defense incurs fitness tradeoffs for interbacterial antagonism" Led by my wonderful team at Academia Sinica!
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
10.03.2025 13:43 — 👍 10 🔁 7 💬 2 📌 0

A҉L҉T҉R҉U҉I҉S҉T҉I҉C҉ ҉Z҉O҉M҉B҉I҉E҉ ҉B҉A҉C҉T҉E҉R҉I҉A҉🦠🧟
Fascinating Nat Comm paper Martin Cann Lab Durham UK
Dead bacteria encode post-mortem protein catabolism via Lon protease—provides nutrients promoting growth of surviving bacteria
No benefit of Lon to live bacteria to account for this
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
14.02.2025 05:52 — 👍 61 🔁 20 💬 2 📌 3
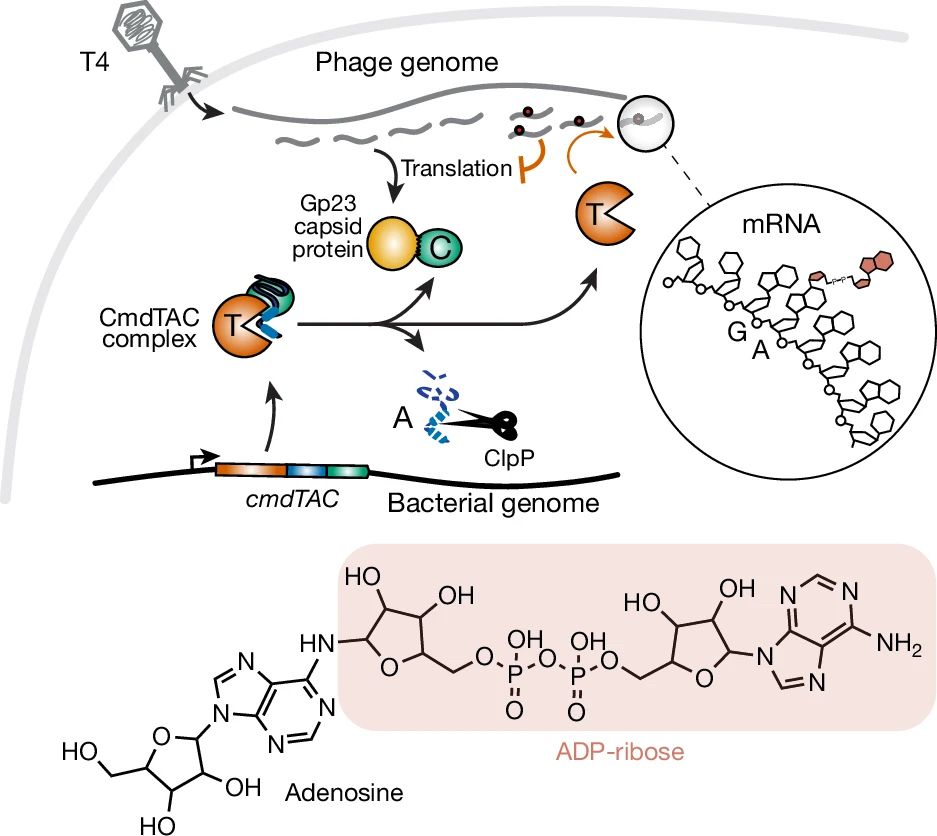
Graphic showing modification of mRNA with ADP-ribose mediated by bacterial enzyme cmdTAC
Check it out! Another novel RNA modification - ADP-ribosylation - that was previously only known on proteins. A cousin to #glycoRNA 👏
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
06.02.2025 19:38 — 👍 223 🔁 81 💬 3 📌 4
Discovery of a distinct BAM complex in the Bacteroidetes https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.01.31.636011v1
02.02.2025 03:18 — 👍 3 🔁 3 💬 0 📌 0
A ubiquitin-like protein controls assembly of a bacterial Type VIIb secretion system https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.01.24.634720v1
25.01.2025 01:19 — 👍 14 🔁 7 💬 0 📌 2
YouTube video by Institute of Molecular Biology 中央研究院 分子生物研究所
Breaking Barriers: Gender Equity in Science at IMB Academia Sinica
Breaking Barriers: Gender Equity in Science, Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taiwan. Together, stronger!
www.youtube.com/watch?v=c4GE...
09.01.2025 12:14 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
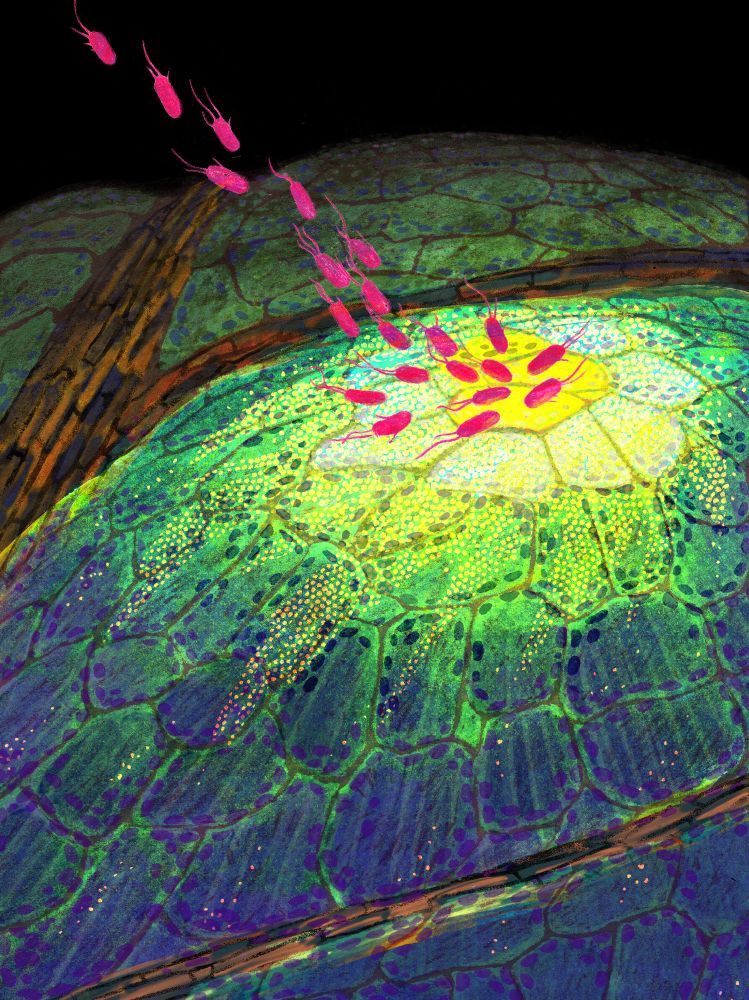
New year, new paper! Now published in @nature.com. We identified and characterised diverse immune cell states in plants under pathogen attack. My postdoc work in the Ecker lab at @salkinstitute.bsky.social. A thread (0/n)
#PlantScience
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
08.01.2025 16:27 — 👍 251 🔁 127 💬 23 📌 6


🚨New review🚨
Evolution and ecology of anti-defence systems in phages and plasmids
Link: www.cell.com/current-biol...
07.01.2025 10:27 — 👍 66 🔁 29 💬 1 📌 0
Ten species comprise half of the bacteriology literature, leaving most species unstudied https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.01.04.631297v1
05.01.2025 08:17 — 👍 57 🔁 40 💬 4 📌 12
Starvation of the bacteria Vibrio atlanticus promotes lightning group-attacks on the dinoflagellate Alexandrium pacificum https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.12.18.629110v1
04.01.2025 23:18 — 👍 5 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
Journal of Cell Science (JCS) publishes cutting-edge science encompassing all aspects of cell biology. JCS is a community journal published by The Company of Biologists (@biologists.bsky.social), a not-for-profit organisation. #cellbiology #cellbio
A platform for life sciences. Publications, research protocols, news, events, jobs and more. Sign up at https://www.lifescience.net.
Assistant Professor at the University of Colorado Boulder. Microbiologist. All-around nerd.
http://colorado.edu/lab/aaron-whiteley/
Associate Editor at Science covering plant science.
Microorganisms and Viruses in the ocean
https://sites.google.com/view/kentotominaga/
Executive Editor/Team Leader Open Access Science Journals Sage Publishing
Opinions = mine
http://linkedin.com/in/jlovick-editor
#oncology #cancerresearch #medicine #biology #cardiology #neurology #microbiology #publichealth #healthcare #technology
PhD student at Trevor Lithgow's group Monash BDI. Facultative bioinformatician who in love with phages and their dark matters.
Assistant Professor at MacEwan University | Bacterial Envelope Enthusiast | She/Her
Tenure-Track PI @nih_nhlbi. Cell biology🔬of non-Mendelian segregation 🧬(meiotic drive) and species barrier in 🐭
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/science/chromosome-dynamics-and-evolution
Incoming Assistant Professor of MCDB at the University of Michigan. Former JCCF and Leading Edge Postdoc Fellow in the Aaron Whiteley lab at CU Boulder. Predatory bacteria and phage enthusiast obsessed with host-pathogen interactions. She/her.
A platform by EMBO that provides independent peer review before journal submission for Refereed Preprints.
Bacteria lover. Good, bad, or other wise. Beneficial, commensal, or pathogenic alike.
Authorized GMB (Genetically Modified Bacteria) scientist
Chemical neurobiologist at Academia Sinica, Taiwan.
http://www.ibms.sinica.edu.tw/wan-chen-lin/
Phytox is a research unit from Ifremer in Nantes working on harmful algae.
https://phytox.ifremer.fr/
Postdoc at UC Berkeley Wolf Lab | PhD Stanford Dassama Lab #bacteria #antimicrobial #resistance 🇹🇼🏳️🌈
Marie Skłodowska-Curie fellow at ISEM Montpellier. Physicist studying complex biological systems - ecosystems, cancer, immune networks and microbial communities.
Editor in Chief of the #NonProfit, #OpenAccess journal @plosbiology.org Former Chief Editor of Nature Microbiology.
#Virologist. #Feminist. #Spaniard in the UK. #Galician. #European always.
Views my own.
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3666-5683
Senior Research Scientist at Stanford Bioengineering | Taking apart and building biology.🧪
Director of Target Discovery Sciences at GSK
Computational biologist | Clinician
PhD @ki.se & @scilifelab.se
Postdoc @crick.ac.uk @sangerinstitute.bsky.social @ebi.embl.org @teichlab.bsky.social
I code in a suit | Nicaragüense | Childless cat lad
🇳🇮🇸🇪🇬🇧🇩🇪
Immunity, insects, viruses, idealism and everything else.
Institut Pasteur
Paris