

Review: AI to advance CRISPR-based genome editing technologies www.nature.com/articles/s41... (read free: rdcu.be/eQKtm)
19.11.2025 12:44 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0

Review: AI to advance CRISPR-based genome editing technologies www.nature.com/articles/s41... (read free: rdcu.be/eQKtm)
19.11.2025 12:44 — 👍 6 🔁 4 💬 0 📌 0I highly recommend this fantastic review by Jennifer A. Korchak, S. Stephen Yi, @nlkproteomics.bsky.social, Nidhi Sahni and Gloria M. Sheynkman!
15.01.2026 14:43 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0And it's a whopper of an issue!
16.12.2025 18:56 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0Walking around the office looking for a print copy yesterday... "Oh yeah, I saw your Stranger Things cover over there..." 😁
27.11.2025 14:47 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
Preprint site arXiv is banning computer-science reviews: here’s why www.nature.com/articles/d41...
11.11.2025 08:43 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0It was a fun one!
03.11.2025 23:37 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0New commentary from @katholt.bsky.social just dropped 😊
03.11.2025 21:43 — 👍 5 🔁 2 💬 0 📌 0
This is figure 1, which shows mutational burden and signature analysis in sperm and matched blood.
The findings of a study in Nature shed light on germline selection dynamics and highlight a broader increased disease risk for children born to fathers of advanced age than previously appreciated. go.nature.com/4h5BglX 🧬 🧪
12.10.2025 19:14 — 👍 22 🔁 10 💬 0 📌 0A reminder that you can follow all of our journals with one click by using our starter pack!
17.03.2025 18:37 — 👍 106 🔁 40 💬 9 📌 4
This was a really nice review to work on:
A genomic view of Earth’s biomes go.nature.com/3VTLImU by Gitta Szabó, Emiley A. Eloe-Fadrosh, Jennifer Pett-Ridge & Tanja Woyke
Thanks, Ursula! X
17.09.2025 06:19 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0🎉 25 years of NRG! Feels a bit bonkers to think I’ve been at the helm for almost 12 years 🤯 Where did the time go???
16.09.2025 19:37 — 👍 9 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0hey bluesky 👋 visa hurdles mean I’m looking for opportunities outside the US. I’m a computational biologist (bacterial + phage genomics, postdoc in Koonin’s group @ NIH). I am interested in teaming up on funding apps. reach out if this resonates!
15.09.2025 17:26 — 👍 70 🔁 90 💬 1 📌 3
Very happy to have contributed to this review on "non-CG" #methylation in animals now out in @natgenet.nature.com. Working again with @obog.bsky.social and Tirsa is always a pleasure. We think this not so well studied form of methylation should be more widely considered, please read: rdcu.be/eFAEk
11.09.2025 10:11 — 👍 44 🔁 16 💬 2 📌 1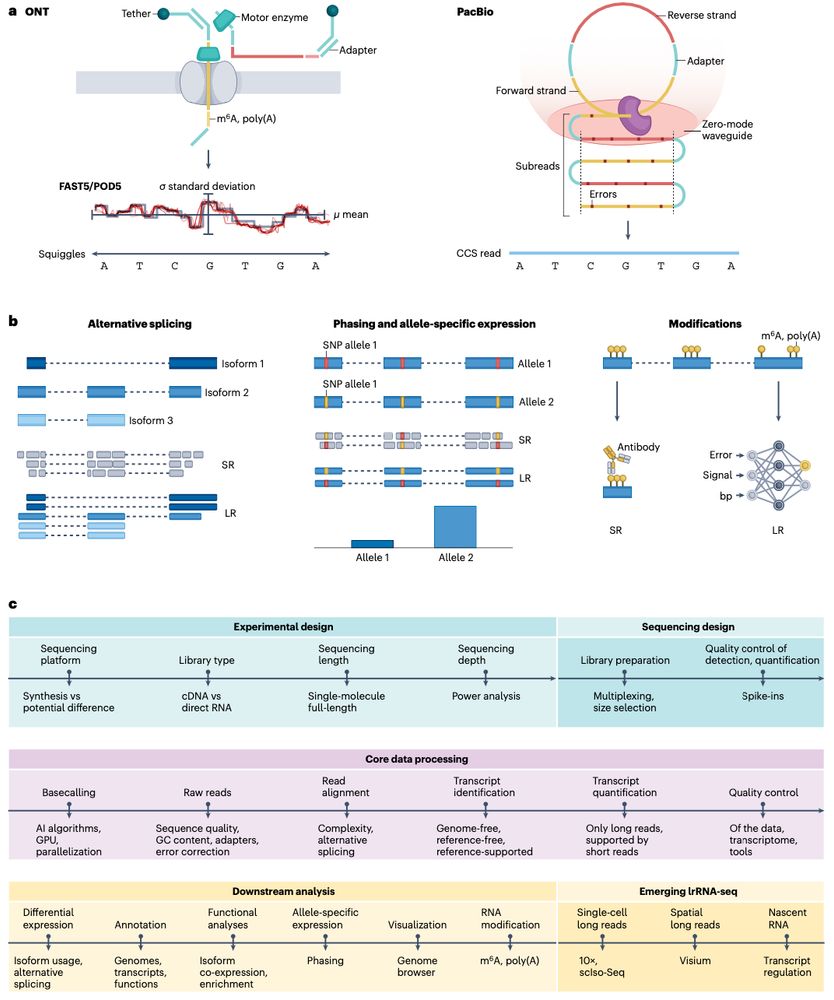
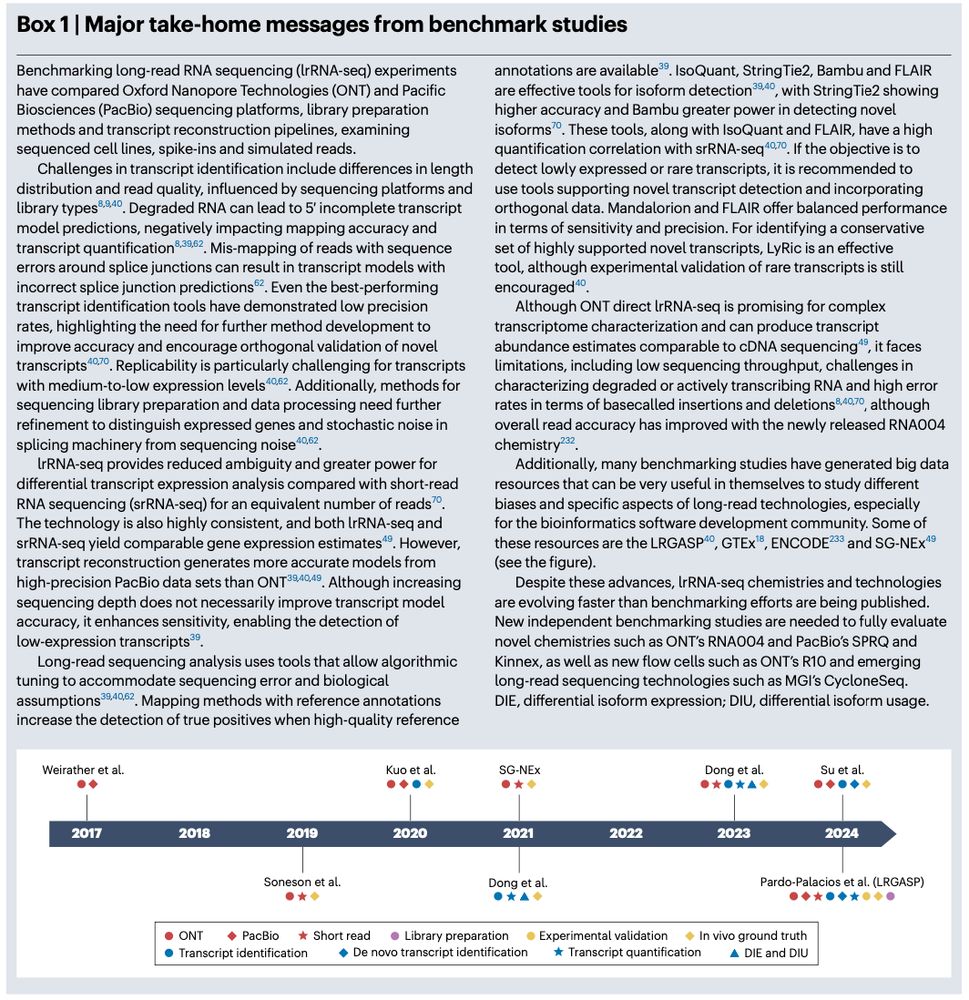
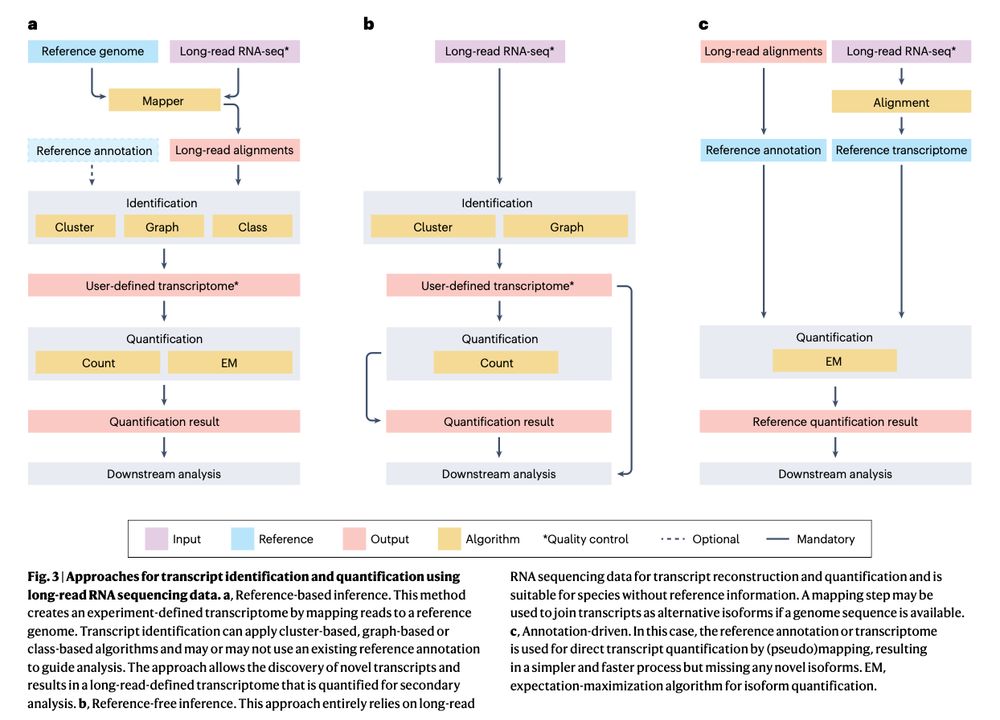
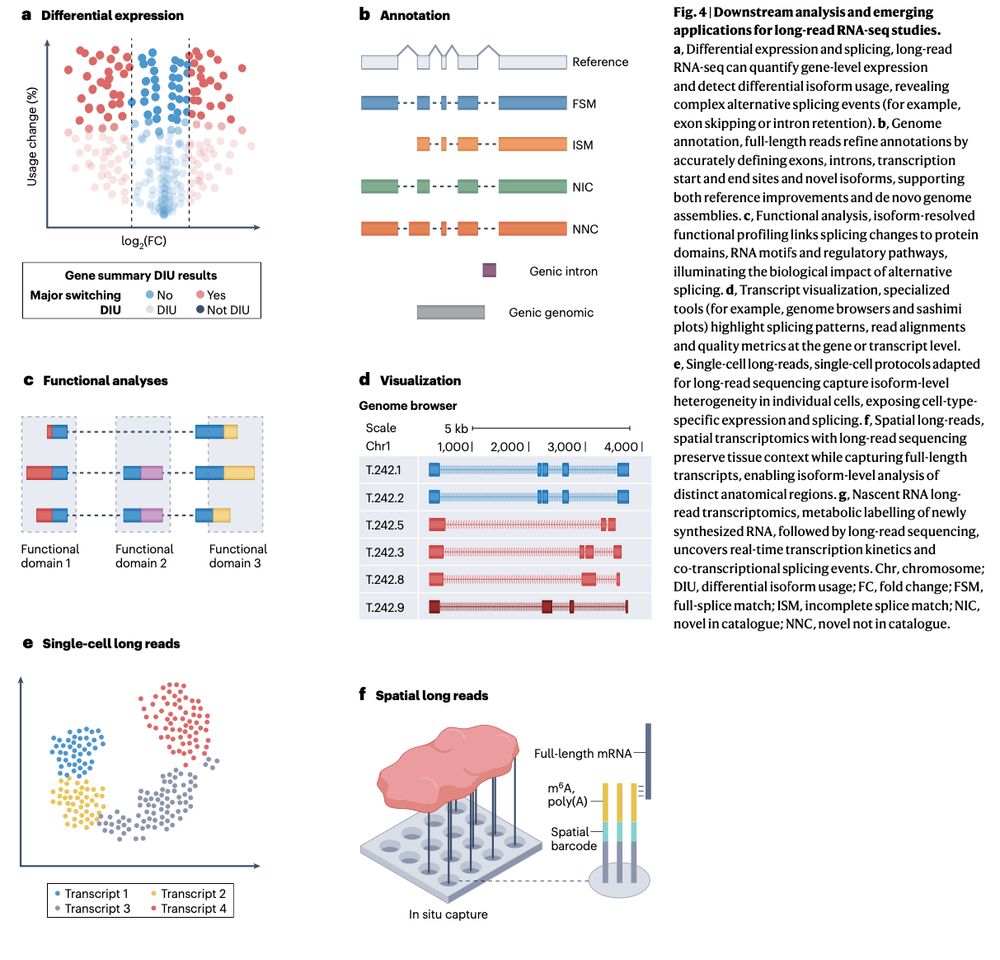
Review: Transcriptomics in the era of long-read sequencing www.nature.com/articles/s41... (read free: rdcu.be/efBjP) 🧬🖥️🧪
29.03.2025 08:57 — 👍 32 🔁 13 💬 1 📌 0
There is a lack of general terminology for translated regions that does not depend on the properties of their products or their sequence.
Spearheaded by Pavel (Pasha) Baranov, this primer provides a unifying nomenclature for translation units: *Translon*
www.nature.com/articles/s41...
I'm not giving up my M-dash!!!
02.09.2025 11:13 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
This is figure 1, which shows a summary of genomic findings for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression.
A Review in Nature Reviews Genetics discusses how genomic advances have enhanced our understanding of schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder, which could address limitations in diagnostic frameworks and future treatment strategies. go.nature.com/44bKTuy 🧬 🧪
23.06.2025 01:31 — 👍 32 🔁 10 💬 0 📌 1
Autophagy genes in biology and disease go.nature.com/4lnHiiT #Review by Hayashi Yamamoto, Sidi Zhang & Noboru Mizushima
26.06.2025 11:07 — 👍 4 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 1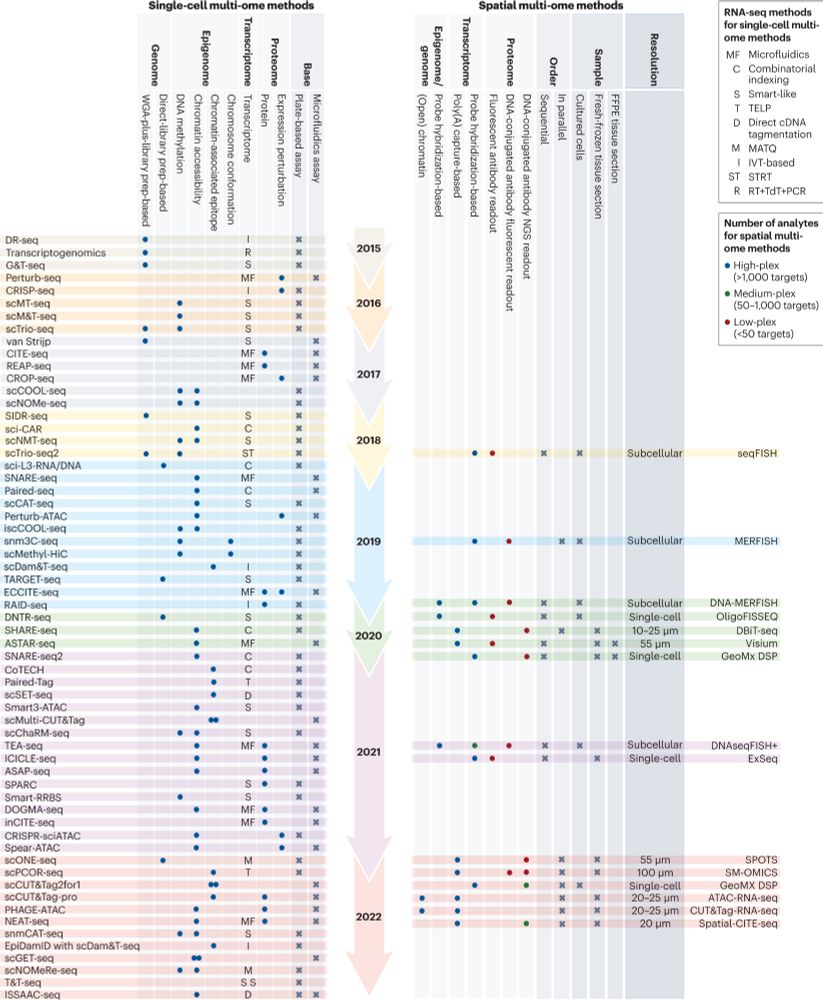
Methods and applications for single-cell and spatial multi-omics go.nature.com/3GkzmzZ #Review by Katy Vandereyken, Alejandro Sifrim, @bernthie.bsky.social & Thierry Voet
Free to read here: rdcu.be/c6JjL

Targeted genome-modification tools and their advanced applications in crop breeding go.nature.com/3T8J8bs #Review by Boshu Li, Chao Sun, Jiayang Li & Caixia Gao
Free to read here: rdcu.be/dFHti
If you enjoyed our RNA splicing collection, this @natrevdrugdiscov.nature.com Review may be of interest:
Protein isoform-centric therapeutics: expanding targets and increasing specificity go.nature.com/44HDClo
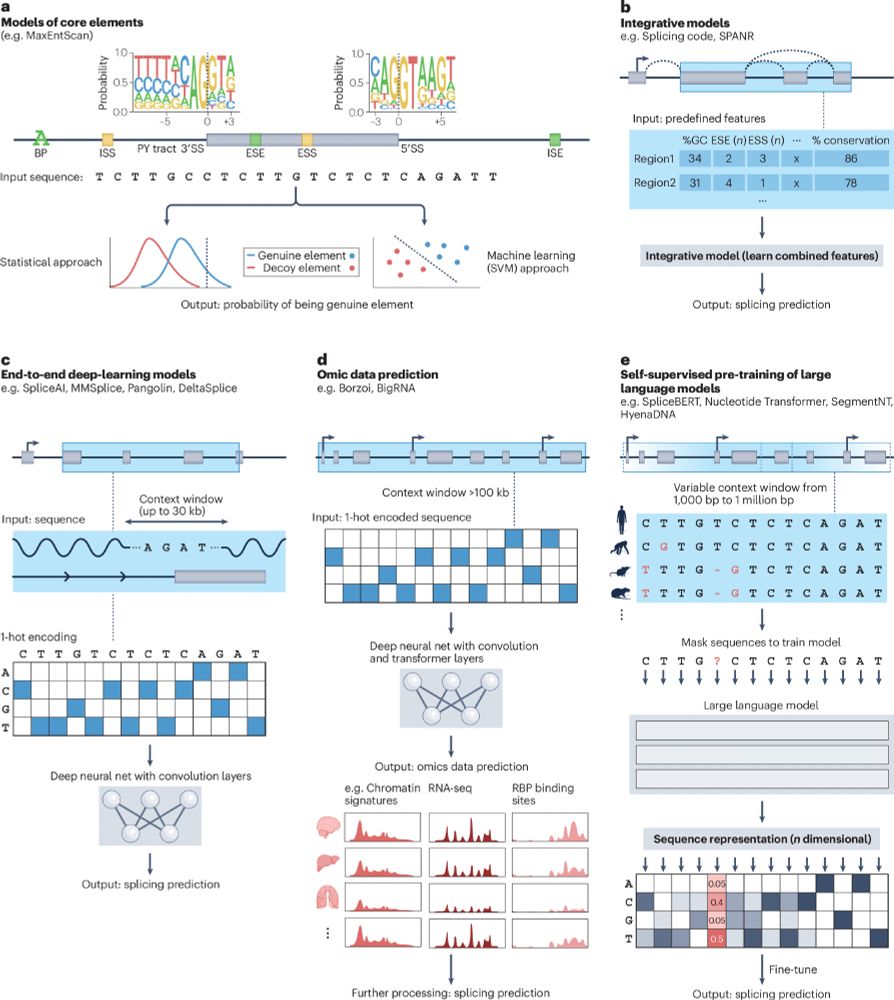
a, Early models built sequence motifs to describe the consensus sequences of individual core splicing elements, such as splice sites (SSs) and intronic and/or exonic enhancers and silencers. Statistical and machine-learning models were built to output the probability of a novel sequence acting as a core splicing element. The sequence logos shown for 5′SS and 3′SS were generated from Human hg38 RefSeq annotations (code available at https://www.github.com/ulelab/splicelogos). b, As our understanding of splicing mechanisms progressed, expert-selected features were extracted from sequences and used to train integrative models to predict splicing outcomes. c, With the advent of deep-learning, models could jointly learn features directly from raw sequence input. Although theoretically, sequence context could be as large as shown in part d, in practice smaller windows of up to 30 kb have been used. d, Supervised models with convolutional and transformer layers produce multimodal genome-wide data. These models use a much larger sequence context and can predict genome-wide data including RNA sequencing coverage, which can be further processed to evaluate splicing. e, By learning how to reconstruct partially masked genomic sequences across multiple species, self-supervised masked language models capture evolutionarily conserved sequence elements and their functional context in a very generic and flexible fashion. The informative numerical representations obtained by large language models can be used for splicing prediction tasks. Here 3′SS within different sequence contexts from multiple species are shown aligned for easier interpretation, but in practice sequences do not have to be aligned. Current masked language models with application to splicing use variable context windows from 1,000 to 1 million base pairs; however, it is currently unclear whether larger context windows confer better performance
Evolution of splicing model architectures go.nature.com/4eweliE
Figure from our recent Review: From computational models of the splicing code to regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications (free to read here: rdcu.be/dVNV4)
What gif pops up when you type your name
15.08.2025 06:40 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Our August 2025 issue is now live: go.nature.com/4kIXzOI
Topics include: systems biology in the single-cell era; ADAR1-mediated RNA editing; retrotransposable element reactivation and its biological impact; transcriptional condensates as temporal signal integrators; X-linked competition
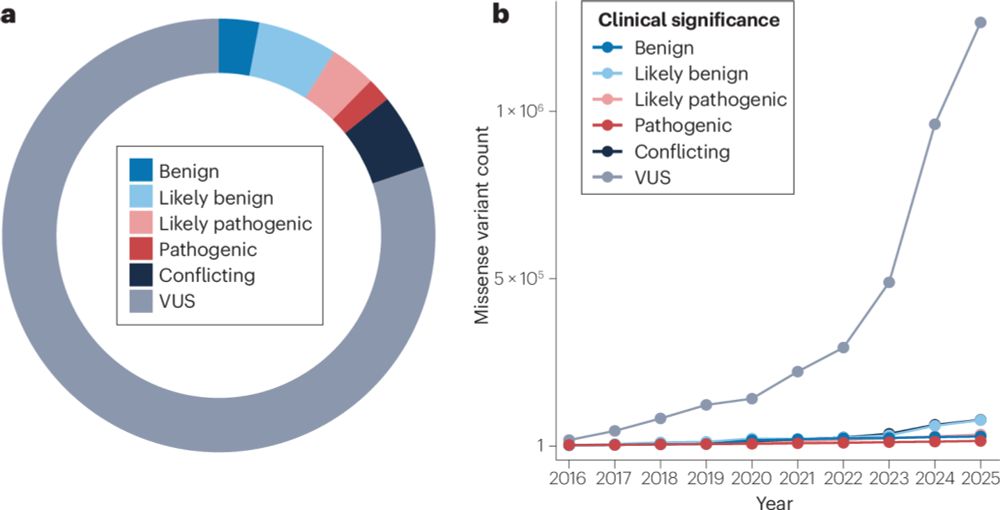
Interested in using functional data to understand clinical variants? Been hunting for a good review of the topic? We just wrote one! rdcu.be/exaEU
21.07.2025 19:33 — 👍 69 🔁 32 💬 0 📌 1We (with Clement Coclet, not on Bsky) had the chance to work on a broad "state of viromics" review. We tried to use this to give an overview of how the field changed over the last ~ 15 years, and also what we think are some of the major remaining challenges. Full-text access at -> rdcu.be/excHt
22.07.2025 15:06 — 👍 84 🔁 41 💬 2 📌 2New review article with @mmdesai.bsky.social is out today! Grateful for the opportunity to contribute something we hope will serve the community well
21.07.2025 17:30 — 👍 47 🔁 15 💬 3 📌 0