
Finally, our model predicts that only the endogenous loci should be affected by loss of H3K27Ac as the ectopic landing pad is located within a chromatin neutral environment. And indeed, CREs like the Xpa enhancer lose accessibility endogenously but not when inserted at the ectopic site. 11/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 1

To test this, we chemically inhibited p300, a histone acetyltransferase that deposits H3K27Ac at a subset of enhancers in mESCs. As predicted, chromatin accessibility dropped, and the amplitude of the drop scaled with the degree of H3K27Ac reduction. 10/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

When we stratified endogenous CREs by their H3K27Ac ChIP-seq signal, we found that the higher the acetylation, the more frequently the chromatin is accessible.
But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Can transcription factors still find and bind their motif at this ectopic site?
Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
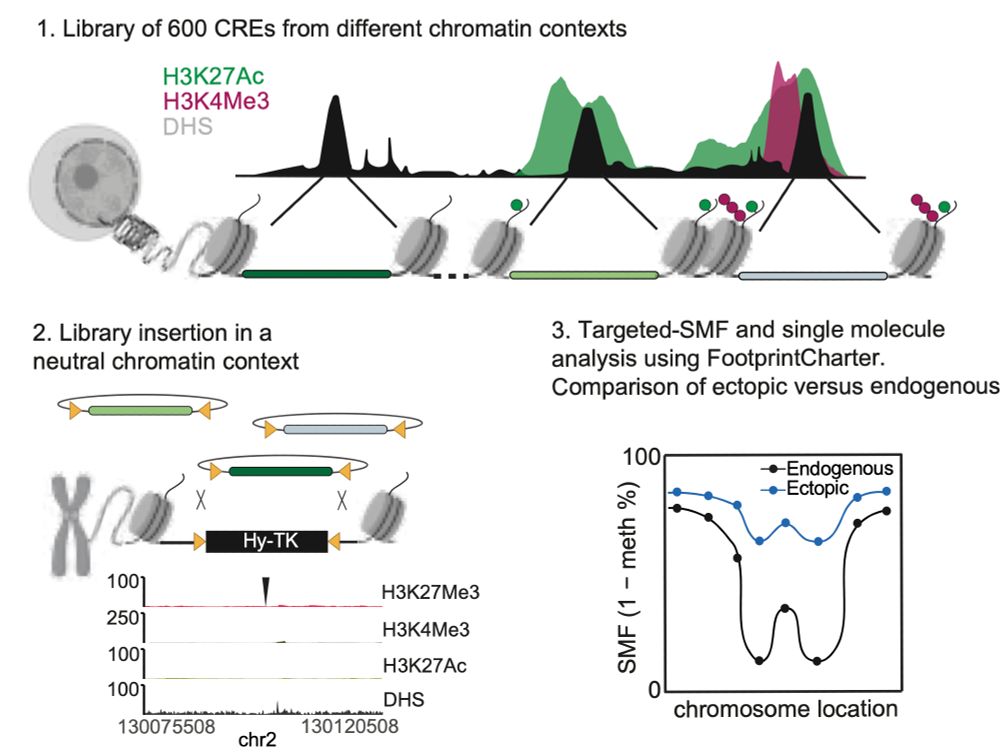
To dissect the contribution of TF binding vs. chromatin context in driving chromatin opening, we developed a Multiplexed Chromatin-Integrated Reporter Assay. It measures the ability of hundreds of CREs (<300 bp) to recruit TFs and establish accessibility at a defined ectopic locus. 7/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We tested this idea by perturbing TF binding. At the motif level, we leveraged the natural genetic variation between mice species crossed into F1 lines. Here, SNPs reduced TF motif affinity across alleles. CREs losing single TF binding showed <10% reductions in chromatin accessibility frequency.6/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We found that the frequency of chromatin accessibility at CREs scales with their increasing number of bound TF motifs. Overall, any additional TF binding event increases chromatin accessibility frequency and width rather moderately, i.e., by ~10%. 5/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We quantified the heterogeneity of chromatin accessibility at mouse ESC CREs. We observed that, within the same cell population, accessible molecules systematically co-exist with nucleosome-occupied ones. At enhancers this is much more prominent than at promoters. 4/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
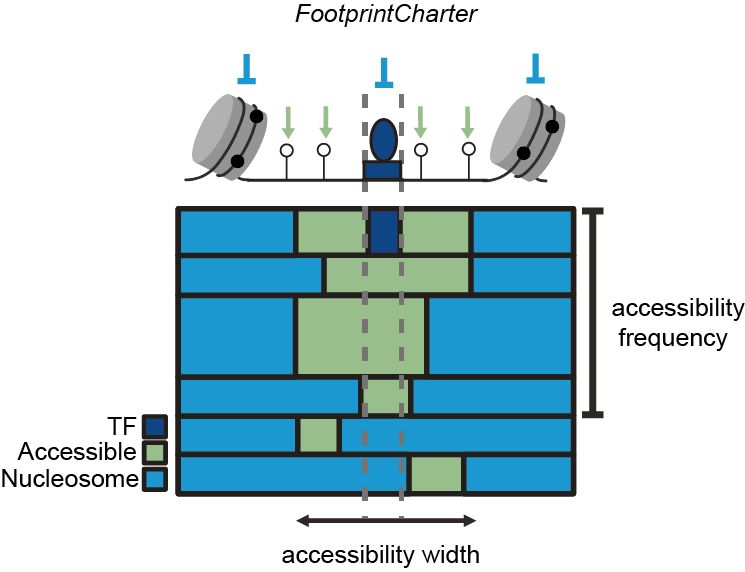
We developed FootprintCharter to classify molecules into accessible or nucleosome-occupied at TF motifs by unsupervisedly detecting TF and nucleosome footprints. FootprintCharter is distributed on Bioconductor at bit.ly/3XLe8RC. For more details, read our annex preprint at bit.ly/3EkRqJh. 3/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 2

Bulk assays such as ATAC-seq selectively sequence accessible loci over nucleosome-occupied ones, losing information on accessibility frequency at CREs. Instead, SMF marks accessibility by methylation footprinting and sequences all molecules, revealing the frequency of accessibility across cells.2/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Happy to share the latest story from @arnaudkr.bsky.social's lab @embl.org! With @guidobarzaghi.bsky.social, we used Single Molecule Footprinting to quantify how often chromatin is accessible at enhancers after TF and chromatin environment changes! Check our preprint bit.ly/3XQMFxN + thread ⬇️ 1/11
08.04.2025 13:51 — 👍 78 🔁 33 💬 4 📌 2

Finally, our model predicts that only the endogenous loci should be affected by loss of H3K27Ac as the ectopic landing pad is located within a chromatin neutral environment. And indeed, CREs like the Xpa enhancer lose accessibility endogenously but not when inserted at the ectopic site. 11/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

To test this, we chemically inhibited p300, a histone acetyltransferase that deposits H3K27Ac at a subset of enhancers in mESCs. As predicted, chromatin accessibility dropped, and the amplitude of the drop scaled with the degree of H3K27Ac reduction. 10/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

When we stratified endogenous CREs by their H3K27Ac ChIP-seq signal, we found that the higher the acetylation, the more frequently the chromatin is accessible.
But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Can transcription factors still find and bind their motif at this ectopic site?
Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

To dissect the contribution of TF binding vs. chromatin context in driving chromatin opening, we developed a Multiplexed Chromatin-Integrated Reporter Assay. It measures the ability of hundreds of CREs (<300 bp) to recruit TFs and establish accessibility at a defined neutral ectopic locus. 7/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We tested this idea by perturbing TF binding. At the motif level, we leveraged the natural genetic variation between mice species crossed into F1 lines. Here, SNPs reduced TF motif affinity across alleles. CREs losing single TF binding, showed<10% reductions in chromatin accessibility frequency.6/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We found that the frequency of chromatin accessibility at CREs scales with their increasing number of bound TF motifs. Overall, any additional TF binding event increases chromatin accessibility frequency and width rather moderately, i.e., by ~10%. 5/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We quantified the heterogeneity of chromatin accessibility at mouse ESC CREs. We observed that, within the same cell population, accessible molecules systematically co-exist with nucleosome-occupied ones. At enhancers this is much more prominent than at promoters. 4/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We developed FootprintCharter to classify molecules into accessible or nucleosome-occupied at TF motifs by unsupervisedly detecting TF and nucleosome footprints. FootprintCharter is distributed on Bioconductor at bit.ly/3XLe8RC. For more details, read our annex preprint at bit.ly/3EkRqJh. 3/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Bulk assays such as ATAC-seq selectively sequence accessible loci over nucleosome-occupied ones, losing information on accessibility frequency at CREs. Instead, SMF marks accessibility by methylation footprinting and sequences all molecules, revealing the frequency of accessibility across cells.2/11
08.04.2025 13:22 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

When we stratified endogenous CREs by their H3K27Ac ChIP-seq signal, we found that the higher the acetylation, the more frequently the chromatin is accessible.
But at the ectopic site, this scaling disappears—suggesting that H3K27Ac enhances accessibility frequency endogenously. 9/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0

Can transcription factors still find and bind their motif at this ectopic site?
Yes! But while they do bind, they typically open chromatin to a lower extent than at their endogenous counterparts—with the notable exception of the insulator CTCF. 8/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

To dissect the contribution of TF binding vs. chromatin context in driving chromatin opening, we developed a Multiplexed Chromatin-Integrated Reporter Assay. It measures the ability of hundreds of CREs (<300 bp) to recruit TFs and establish accessibility at a defined neutral ectopic locus. 7/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We tested this idea by perturbing TF binding. At the motif level, we leveraged the natural genetic variation between mice species crossed into F1 lines. Here, SNPs reduced TF motif affinity across alleles. CREs losing single TF binding showed<10% reductions in chromatin accessibility frequency. 6/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We found that the frequency of chromatin accessibility at CREs scales with their increasing number of bound TF motifs. Overall, any additional TF binding event increases chromatin accessibility frequency and width rather moderately, i.e., by ~10%. 5/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We quantified the heterogeneity of chromatin accessibility at mouse ESC CREs. We observed that, within the same cell population, accessible molecules systematically co-exist with nucleosome-occupied ones. At enhancers this is much more prominent than at promoters. 4/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

We developed FootprintCharter to classify molecules into accessible or nucleosome-occupied at TF motifs by unsupervisedly detecting TF and nucleosome footprints. FootprintCharter is distributed on Bioconductor at bit.ly/3XLe8RC. For more details, read our annex preprint at bit.ly/3EkRqJh. 3/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Bulk assays such as ATAC-seq selectively sequence accessible loci over nucleosome-occupied ones, losing information on accessibility frequency at CREs. Instead, SMF marks accessibility by methylation footprinting and sequences all molecules, revealing the frequency of accessibility across cells.2/11
08.04.2025 12:54 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
PhD student @EMBL in the Krebs Lab
PhD Candidate @embl.org | European Molecular Biology Laboratory | Duss and Hennig groups
#RNA structure and dynamics | #single-molecule | #biophysics | #structuralBiology | #translation | #biochemistry
NYU postdoc with Tsirigos and Aifantis labs.
Former EMBL Heidelberg PhD with Krebs and Zaugg labs.
Group leader at EMBL Heideberg
https://www.embl.org/groups/krebs/
Postdoc Krebs Lab @EMBL Heidelberg
Joint with Kundaje Lab @Stanford
Previously PhD Schulz Lab @MPI-MG
Postdoctoral Fellow, Genome Biology Unit, EMBL Heidelberg
Statistician, Computational Biologist, R |> Bioconductor
https://www.huber.embl.de
Textbook: Modern Statistics for Modern Biology https://www.huber.embl.de/msmb/ (with @sherlockpholmes.bsky.social)
Postdoctoral fellow at @EMBLHeidelberg
@arnaudkr.bsky.social
, interested in TF occupancy, 3D organization, genomics, epigenetic, gardening and much more
Molecular Biologist, Transcription enthusiast and stem cell afficionado
Associate Professor at Max Perutz Labs and University Vienna,
PI @ Gladstone Institutes & UCSF. Molecular technologies & the genomics / molecular biology / biochemistry of gene regulation. Views here mine & do not represent those of my affiliated institutions.
Head of Genome Biology Dept @EMBL,
Scientist, Principal investigator, Professor
Exploring genome regulation during development,
and everything to do with enhancers.
3D genome, chromatin topology,
cell_fate, embryonic Development,
Single Cell genomics
Nature Genetics is a monthly journal publishing high impact research in genetics and genomics. Part of @natureportfolio.bsky.social
Repost/like=interesting/relevant, not necessarily endorsement.
PhD student @EMBL, Stegle group.
Deep learning on single-cell genomics, genetics and electronic health records to understand disease and improve human health.
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-1674-5141
Passionate about (epi)genomics and chromatin biology.
Postdoc at @ifomresearch.bsky.social (Milan 🇮🇹) @LabPagani //
@AIRC_it & @MSCActions Fellow //
Alumnus @embl.org (Heidelberg 🇩🇪)
🔬🧬🦕
📣 Latest: tinyurl.com/H33K9AK27A
The European Molecular Biology Laboratory drives visionary basic research and technology development in the life sciences. www.embl.org
"Docet (omnes) omnia" 😊
Enseigner (à tous) le savoir en train de se constituer dans les #Sciences, les #Arts & #Lettres | Université PSL | www.college-de-france.fr
👩🔬 The Institut Pasteur is a leading global biomedical research institute.
🔬 Explore with us the frontiers of biomedical research
🧪 Follow us to uncover groundbreaking discoveries
🌍 Join a community passionate about progress and open science
🌐 Internationally renowned #Research Center
🏥 State-of-the-art Hospital Group
🇨🇵 France's leading #cancer center
curie.fr
Computational biologist interested in deciphering the genomic regulatory code at vib.ai











