I'm excited to share that we've received a NIBIB Trailblazer Award to advance our work on engineering therapeutic macrophages! Grateful for our team and excited to launch this collaboration with the Caleb @bashorlab.bsky.social at Rice!
01.08.2025 11:14 — 👍 24 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Thank you @njmicrobe.bsky.social for this really nice writeup about our work!
26.06.2025 19:27 — 👍 7 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Many thanks to many members of the Yang Lab who contributed to this project (including many undergrads!) and to our collaborators Douglas McCloskey and Xiaoyang Su! 11/11
@njms-mdphd.bsky.social
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
We're eager to explore these topics in future projects and to see how generalizable these phenotypes are to pathogenic E coli and other species. We think these mechanisms may inform design of antibiotic adjuvants that can slow or prevent resistance development. 10/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
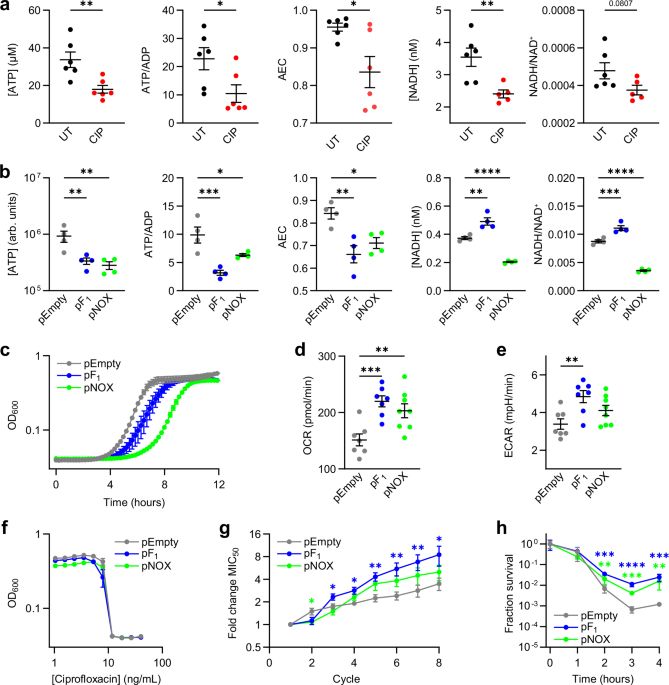
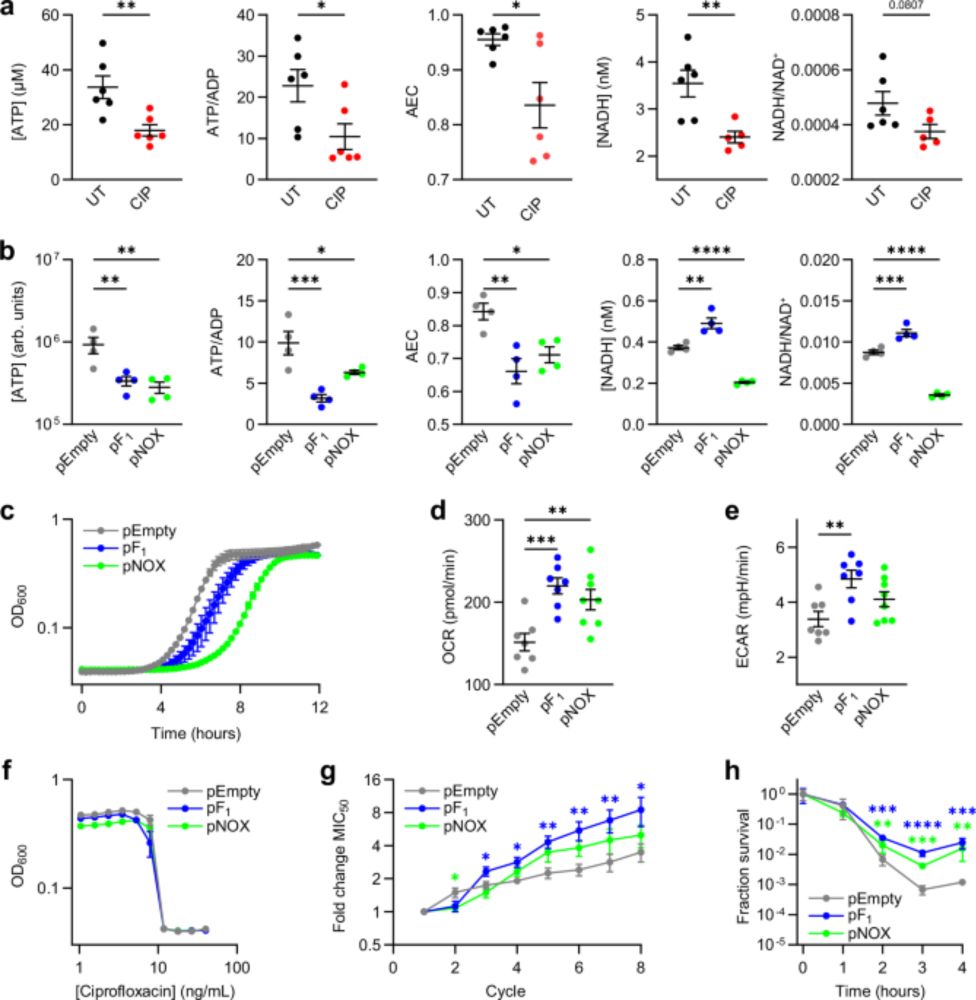
Importantly, little is known on how energy balance alters bacterial physiology. Although metabolic stress is known to inhibit growth and enhance metabolism, our work is the first to study stress responses and antibiotic phenotypes caused by disrupted energy balance. 9/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
By developing a new assay, Barry showed that mismatches between ATP utilization and production (disrupting ATP homeostasis) are sufficient for augmenting antibiotic killing. Thus, Barry's work introduces new concepts in understanding the interplay between energy balance and antibiotic efficacy. 8/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Using bacterial genetics approaches, Barry was able to show that bioenergetic stress mechanistically induces stress responses that increase antibiotic stress-induced mutation rates and that protect against antibiotic killing. 7/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
This was also surprising that we previously showed that high levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were associated with high antibiotic killing, but the pF1 and pNOX cells had decreased killing while also possessing high levels of ROS! 6/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Correlations between ATP availability and persistence are known and are usually thought about as correlations between metabolic activity (e.g., dormancy, low ATP) and killing efficacy. But Barry's cells have HIGH metabolic activity, which we previously found to INCREASE antibiotic killing. 5/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Surprisingly, Barry found that bioenergetically stressed cells evolve antibiotic resistance FASTER than control cells (!!) and are also in general protected from bactericidal antibiotic stress (persistence). 4/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
These strains constitutively hydrolyze ATP (pF1) or NADH (pNOX), creating ATP or NADH sinks in these cells. These in turn induce 'bioenergetic stress' in which the cells are always struggling to meet their energetic demands. 3/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Barry generated a genetic model system (frequently used by the metabolic engineering community) involving E coli cells over-expressing ATP synthase F1 complex genes (pF1) or heterologously expressing NADH oxidase from Streptococcus (pNOX). 2/n
09.06.2025 19:15 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Honored to receive this year's Young Investigator Award from our local ASM branch!
14.05.2025 22:08 — 👍 10 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Yang Lab had a terrific time at Rutgers' Biomedical Health Informatics and Artificial Intelligence Symposium yesterday. Great jobs by Yiqi Yan, Oliver Gu, and Reuven Rosen who presented on their work!
14.05.2025 12:16 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
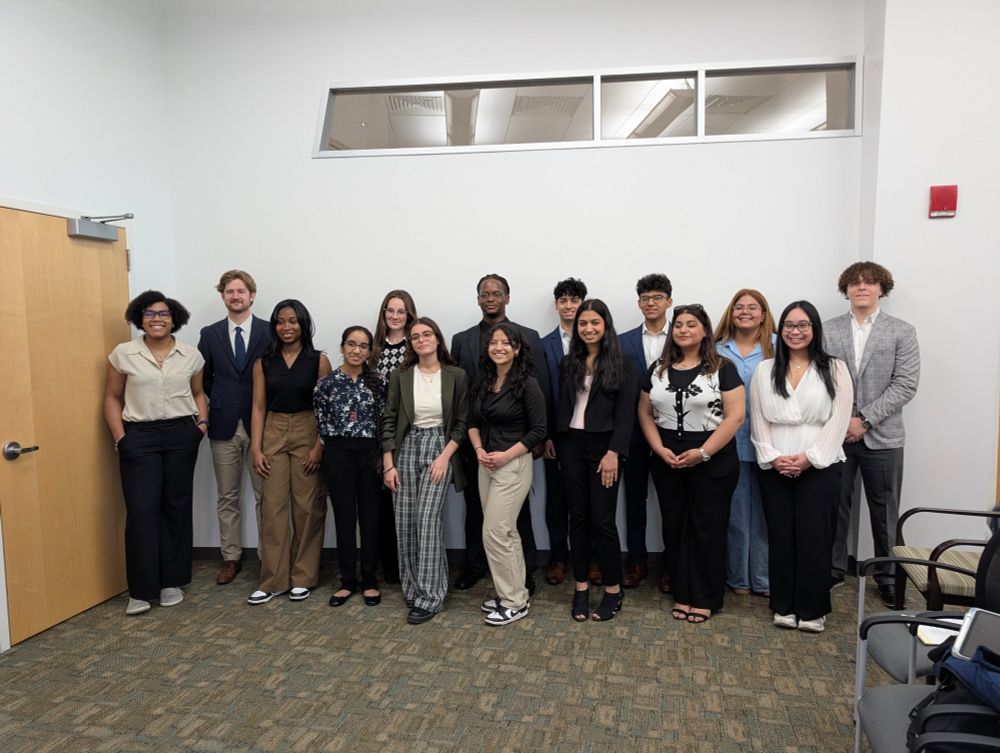


Our undergraduate machine learning maestro Edson Petry gave a terrific research presentation this afternoon at the Rutgers Pathways for Junior Scientists Research Program! #Rutgers #NJMS
06.05.2025 03:50 — 👍 4 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Would you mind adding me too please? Thanks in advance!
04.05.2025 20:59 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
I'm so proud of my technician Lia Goodwin who presented a poster at her first conference at the CSHL Systems Immunology meeting yesterday!
24.04.2025 17:45 — 👍 15 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Terrific work by Ethan Bustad, Edson Petry, Oliver Gu, Braden Griebel, and Tige Rustad and wonderful support from our collaborator David Sherman (U Washington)! @rutgershealth.org 6/6
03.04.2025 18:41 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
We are now using this work as a launching point for studying how individual (clinical) strains survive host and antibiotic stress and are eager to collaborate if you have some interesting phenotypes that you think are geneically regulated! 5/n
03.04.2025 18:41 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We found that transcription factor activities are better predictors of fitness under hypoxia than TF expression alone. Moreover, these analyses demonstrated that interpretable machine learning can reveal transcriptional programs causally regulating fitness under stress. 4/n
03.04.2025 18:41 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
We performed gene regulatory network analyses to directly infer transcription factor activities from gene expression profiles. Using data from a TF over expression screen (TRIP), we trained an interpretable machine learning model that predicts Mtb fitness from RNA expression. 3/n
03.04.2025 18:41 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Pathogens live in hostile environments and must activate transcriptional stress response programs to survive exogenous stressors. In work led by Ethan Bustad, we sought to study Mtb fitness under hypoxic stress using systems biology approaches. 2/n
03.04.2025 18:41 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Frontiers | Predicting fitness in Mycobacterium tuberculosis with transcriptional regulatory network-informed interpretable machine learning
Ever wonder how Mycobacterium #tuberculosis deals with stressful environments? I'm pleased to share that in a second piece of good news this week, our recent work in collaboration with Shuyi Ma (Seattle Children's) was published at Frontiers in Tuberculosis. 1/n
www.frontiersin.org/journals/tub...
03.04.2025 18:41 — 👍 6 🔁 2 💬 1 📌 0
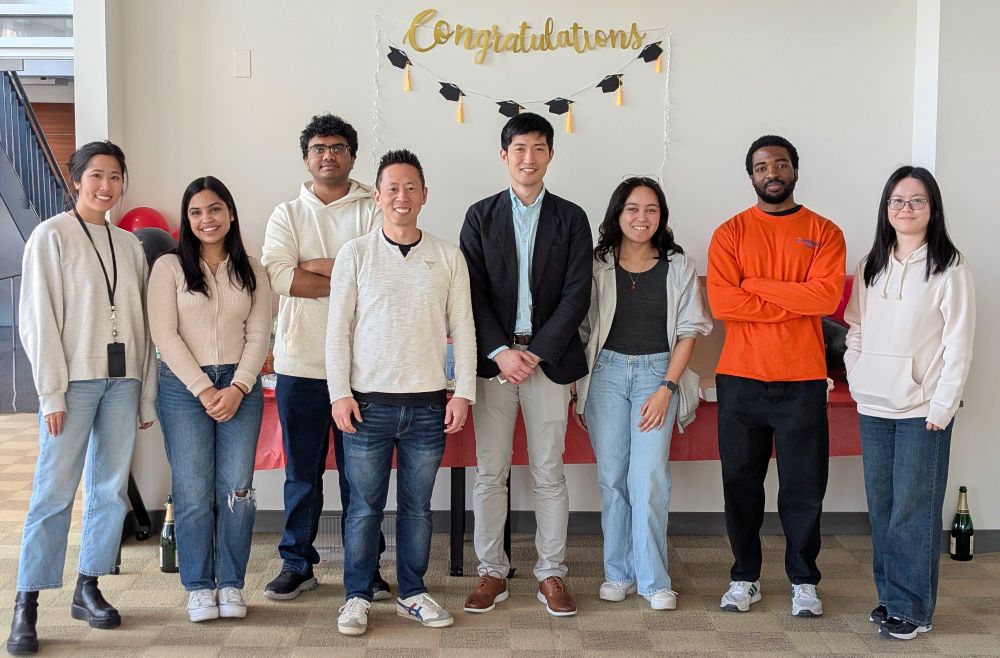

I am thrilled to share that our rock star MD/PhD student Barry Li successfully defended his PhD today entitled "Bioenergetic stress potentiates antimicrobial resistance evolution and persistence"! Barry is our first student to finish his PhD and I am so incredibly proud of him!
02.04.2025 18:29 — 👍 11 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
👋 Can I please join also?
18.11.2024 01:44 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Researching WGS/Epi/Taxonomy of pathogenic mycobacteria and evo of microbiomes. Irish-born, Nottingham-working. Call me Conchúr if you can pronounce it. He/They
https://www.ntu.ac.uk/staff-profiles/science-technology/conor-meehan
Associate Prof. in Molecular Bacteriology - #Tuberculosis #Mycobacteria research. Based at the Royal Veterinary College UK.
Microbiologist fighting tuberculosis with mucosal immunity and sequencing techniques | Assist. Instructor @ UTSW | Avid but slow runner | Husband, brother, son and good friend |
Research Director in Medicinal Biochemistry (mycobacteria, Mtb, M.abscessus, antibacterials, lipolytic enzyme inhibitors, medicinal chemistry, chemobiology) at LISM UMR7255 CNRS, Marseille
https://tuberculosis-lbp.wixsite.com/tuberculosis-lbpteam/lbp-team
Virologist & Professor, Pitt Dept. of Microbiology & Molecular Genetics and former Director of @Pitt-PMI.bsky.social
Seattle native living in Pittsburgh.
Website: http://ambrose-lab.com
Infectious Disease Professor (Immunocompromised Host/ Transplant ID) at Stanford University.
Recent PhD grad @tobinlab.bsky.social | Studying basic cell bio of mycobacterial infection using zebrafish and macrophages 🐠🔬
Posts reflect my own thoughts and opinions and do not represent the opinions of my employer or other affiliates.
Royal Society University Research Fellow | NUAcT Fellow @ Newcastle University
Investigating mycobacterial transport systems
#structuralbiology #microbiology
Instagram @kshbeckham
Director of the Translational Research Unit of the National Institute for Infectious Diseases, Rome, Italy.
Team dedicated to R&D of novel antibiotics to fight Antimicrobial resistance
The Global TB Program at Texas Childrens and @bcmhouston.bsky.social focuses on #TB prevention, diagnostics, treatment, & immunology under the direction of Dr @annamandalakas.bsky.social #TBSky
MD, PhD. Fighting #tuberculosis.
An outdoorsy immunologist & microbiologist | Assistant Professor at @LSUHS_Micro | Tuberculosis and Cancer | ScRNAseq | Immunometabolism
Cell aims to publish the most exciting and provocative research in biology. Posts by Scientific Editors on the Cell editorial team. See the latest papers at https://www.cell.com/cell/
❤️ Physics, Molecular Biology, Automated DNA Sequencing, Bioinformatics, Biomarker Discovery. SwiftUI.
Postdoctoral Fellow, Biomedical Engineering
University of Delaware
Newark, United States
Mtb enthusiast, Host-pathogen researcher at BWH. ex-New Yorker, Bostonian becoming
🇨🇳🇺🇸🌈
Gut physiologist studying epithelial-immune dysfunction in the gastrointestinal tract 🧪 gutsciencelab.com
🔬 #organoids #macrophages #stemcells #ibd
Assistant Professor at @isbscience.org studying single-cell lifestyles of bacteria.