
I am excited to share that Michelle's (Hui Wen) PhD work on microbial subversion of innate immune and cell death pathways is now online! Congrats @michelleyeaphw.bsky.social and all co-authors! 🥳
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
@kaiwenchen-lab.bsky.social
Assistant Professor in NUS Singapore. Cell death, innate immunity and host-pathogen interaction.

I am excited to share that Michelle's (Hui Wen) PhD work on microbial subversion of innate immune and cell death pathways is now online! Congrats @michelleyeaphw.bsky.social and all co-authors! 🥳
www.embopress.org/doi/full/10....
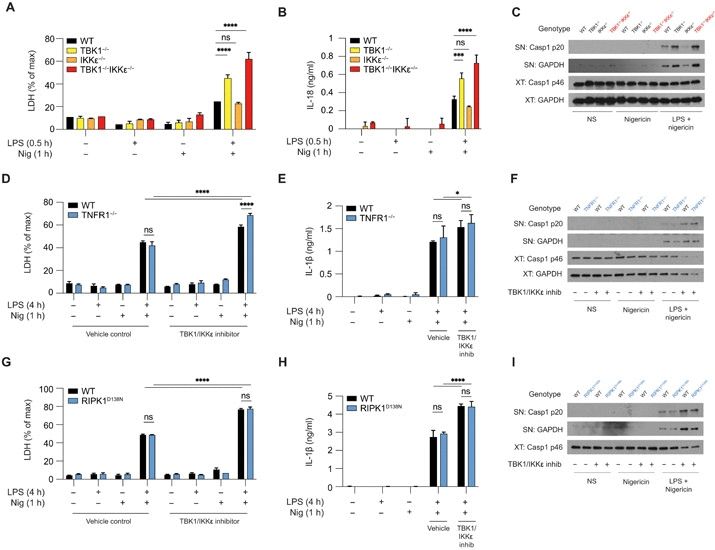
The loss of TBK1, or both TBK1 and the related kinase IKKε, results in uncontrolled cell death–driven inflammation. We show that TBK1/IKKε prevent premature cell death by limiting the activity of multiple death pathways in myeloid cells. www.science.org/doi/10.1126/...
07.03.2025 20:49 — 👍 52 🔁 22 💬 7 📌 4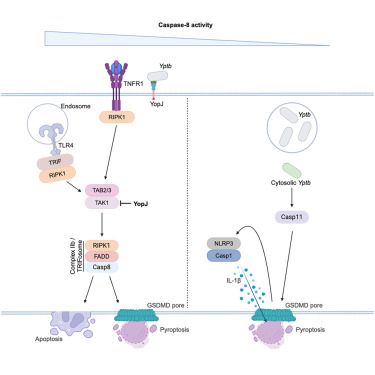
Thrilled to start 2025 with our latest findings! Yersinia invades macrophage cytosol to activate caspase-11 when caspase-8 or YopJ are inactive. www.cell.com/cell-reports...
16.01.2025 23:09 — 👍 30 🔁 12 💬 2 📌 0Thank you!
14.12.2024 10:24 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
We just posted a preprint about a death mechanism that we find truly surprising.
When you turn off transcription, cells die (duh!)... but did you know this happens due to loss of Pol II itself, not loss of Pol II activity!?!
preprint here and a thread (1/n): www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1...
🧪
I would love to join this group if possible? Thank you !
13.12.2024 13:55 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0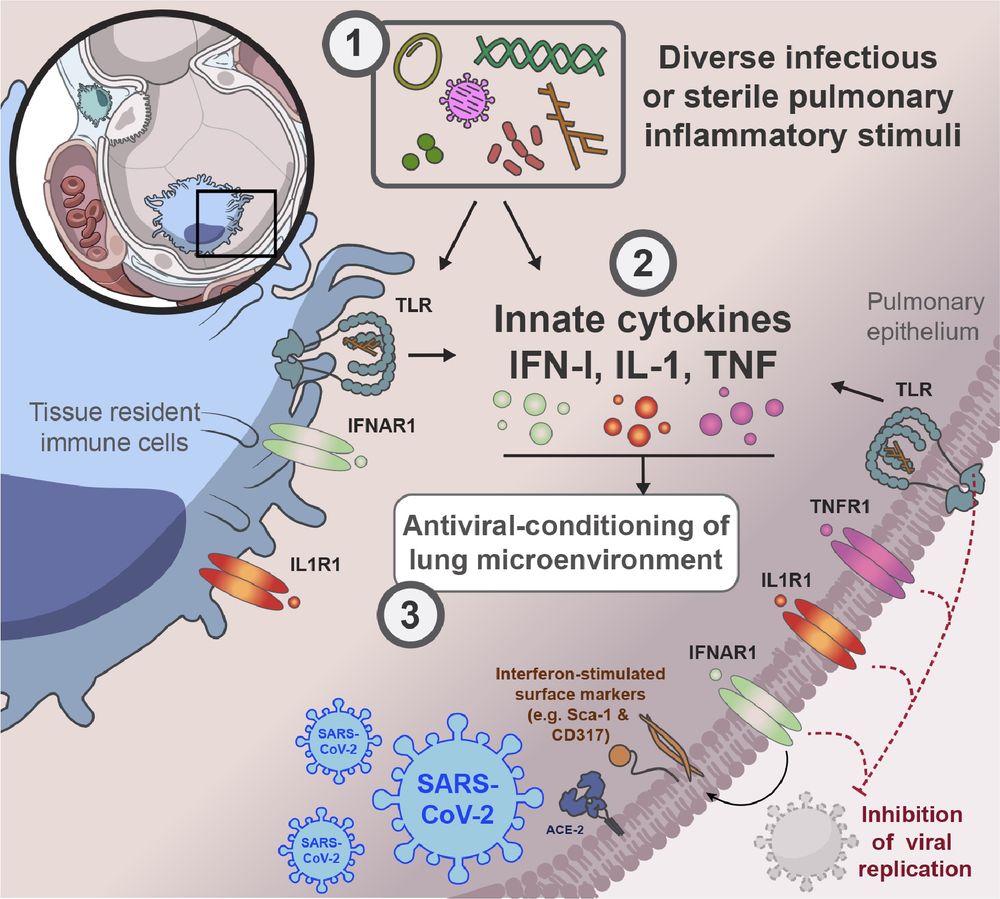
Graphical summary of our paper. In mice, prior lower airway exposure to diverse inflammatory stimuli, including chronic bacterial infections such as M. tuberculosis, acute bacterial infections such as pulmonary S. aureus, viral infections such as Influenza A, type-II allergic responses such as the OVA-Alum model, activation of pulmonary TLR9 by CpG or pulmonary TLR1/2 by Pam3CSK4 leads to reduced viral burden upon subsequent infection with SARS-CoV-2 (SCV2). (2) This SCV2 restriction occurs prior to induction of SCV2-specific adaptive immune responses and is mediated through innate immune responses, including the induction of IFN-I, TNFα and IL-1 and sustained changes to the TRM (Tissue resident macrophage) cellular compartment and the pulmonary epithelium. (3) Innate cytokine and TLR signaling to both recruited immune cells and the pulmonary epithelium creates a microenvironment in the lung that limits early replication of SCV2. IFN-I signaling to pulmonary ECs (epithelial cells) increases expression of interferon-stimulated genes, that likely cell-intrinsically limit viral replication. TNF- or IL-1 suppress SCV2 independently of IFN-I signaling. TNF acts exclusively through radio-resistant cell types such as the lung epithelium, whereas IL-1 affords control both direct and indirectly, through either stromal and hematopoietic cell types, to restrict overall early SCV2 burden.
Best #Nikolaus 🎅! Our paper on how the 🫁 microenvironment can shape #innate immunity against #viruses is out @sciimmunology.bsky.social This was a herculean effort brilliantly led by @pauljbaker.bsky.social who singlehandedly established the model in the lab during the pandemic. 🧪 #Immunosky 1/9
06.12.2024 22:37 — 👍 294 🔁 83 💬 28 📌 9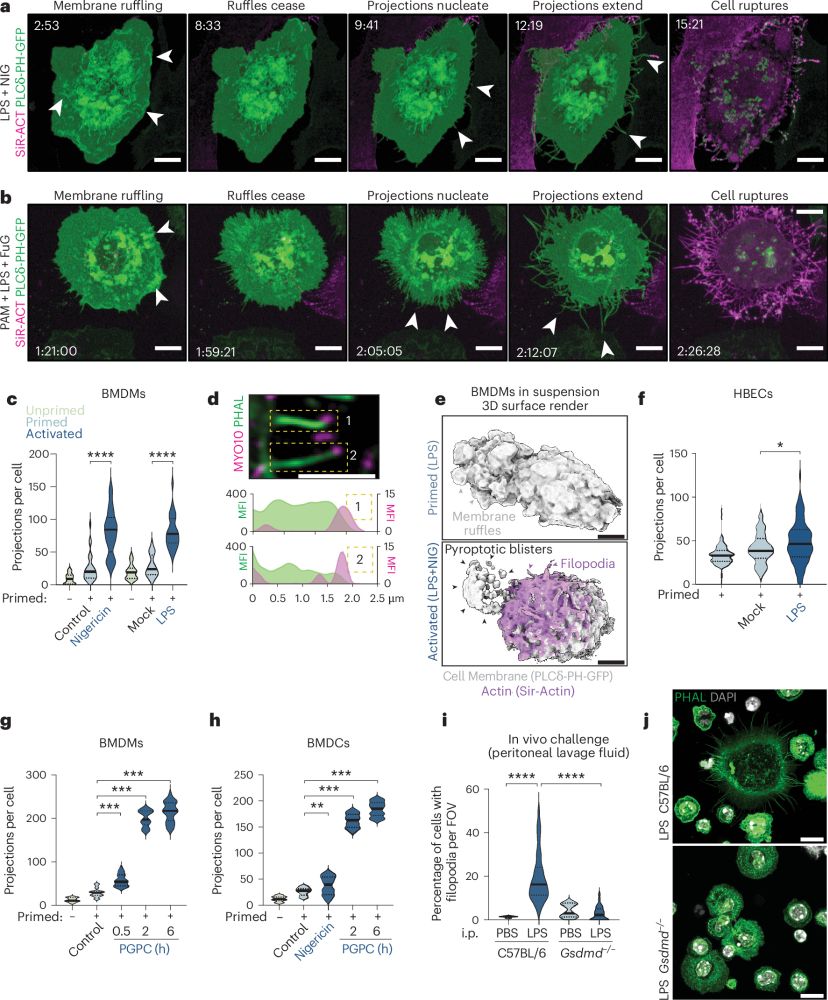
Have you ever wondered whether pyroptotic corpses have functions beyond the grave? We made the surprising discovery that pyroptotic corpses are flagged by #filopodia to alert #DendriticCells they need autopsy. A short Bluetorial (1/13)👇with movies!
Link: rdcu.be/d2mjm
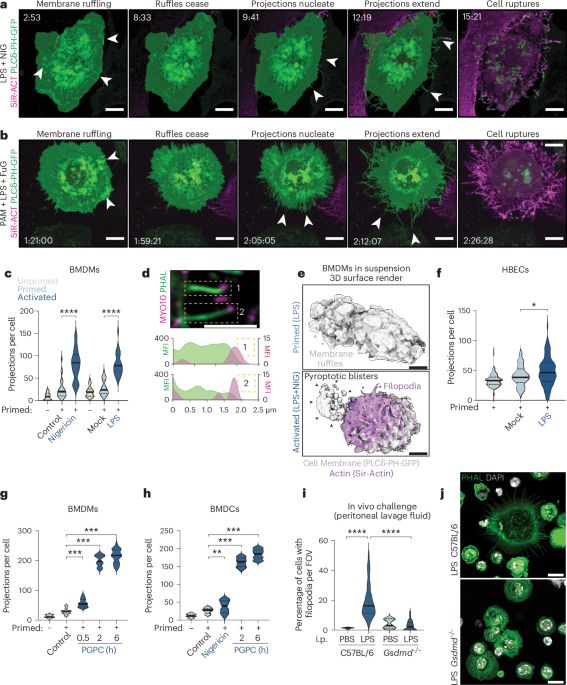
#NoTimeToDie! @inflammasomelab, Holley, Monteleone &co show @natimmunol.bsky.social that cells that die by #pyroptosis, or #necroptosis, are crowned with F-actin filopodia that makes them visible by dendritic cells via CLEC9A to initiate adaptive immunity! www.nature.com/articles/s41...
05.12.2024 16:55 — 👍 59 🔁 22 💬 1 📌 1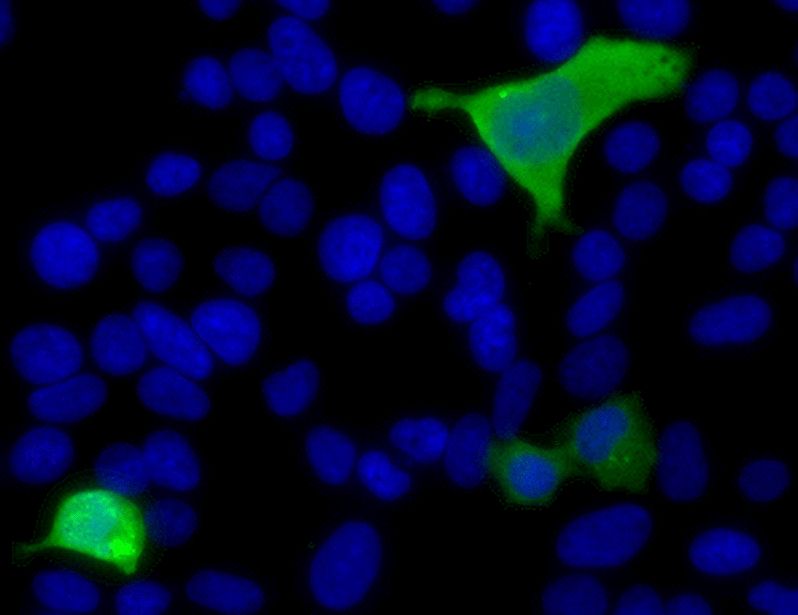
Thrilled to share our new paper out today in #ScienceImmunology!
It’s been a long time coming and I’m so excited to be able to share it.
Skeetorial (is that what we call it here?) to come when it is (a) not Saturday and (b) not my birthday. Best present ever!
#ImmunoSky #RNASky