Congrats Courtney and the team! Very interesting work.
23.07.2025 06:25 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

Oldies but Goldies. from 2007. Light-powering Escherichia coli with proteorhodopsin www.pnas.org/doi/10.1073/...
10.06.2025 12:56 — 👍 3 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0
@arielchazan.bsky.social @galitzlil.bsky.social
31.05.2025 12:57 — 👍 5 🔁 1 💬 0 📌 0
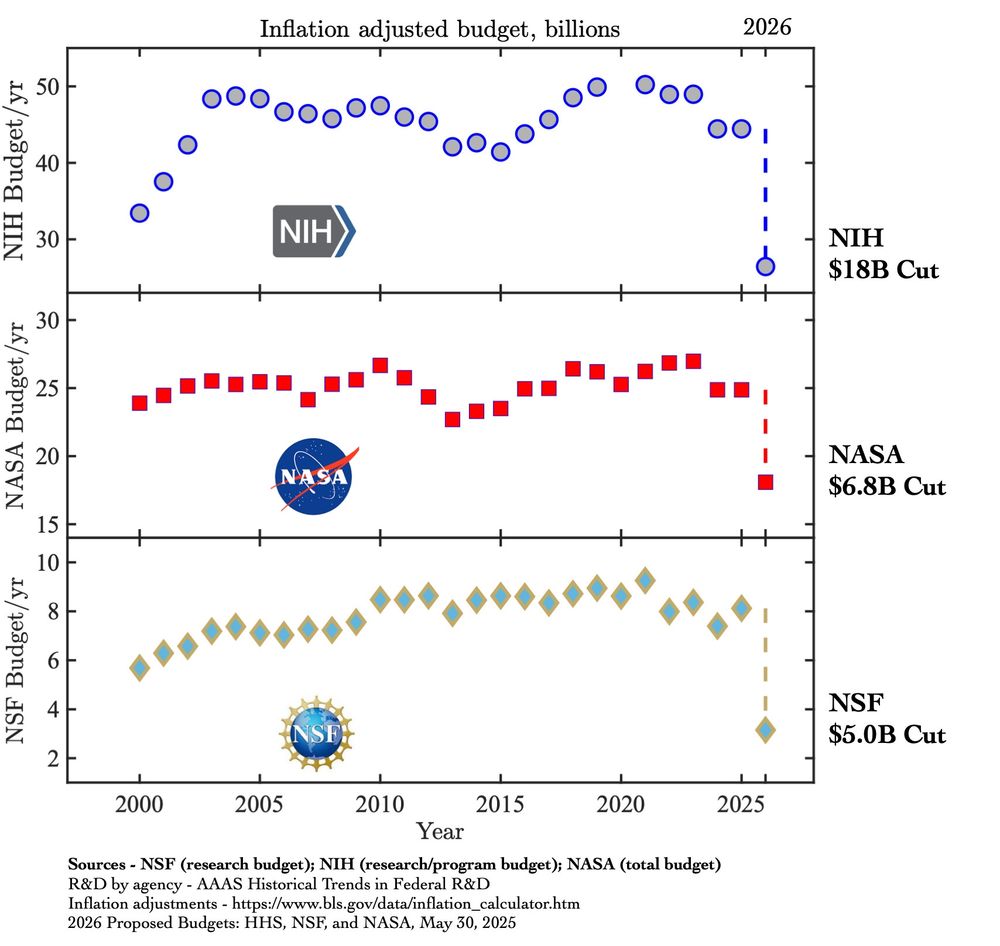
Graphs showing 25 years of budgets for the National Institute of Health, NASA, and the NSF. In all cases, the proposed budget for next year is far, far below any year of the previous quarter century.
There are 2 previous historical cases of countries destroying their science and universities, crippling them for decades: Lysenkoism in the USSR and Nazi Germany. The Trump administration will be the 3rd.
It's not just budgets but research, institutions, expertise, and training the next generation.
31.05.2025 04:43 — 👍 15293 🔁 7915 💬 455 📌 533
Super cool work on the function of intrinsically disordered regions in regulating transcription factor DNA binding.
28.05.2025 10:53 — 👍 13 🔁 7 💬 1 📌 0
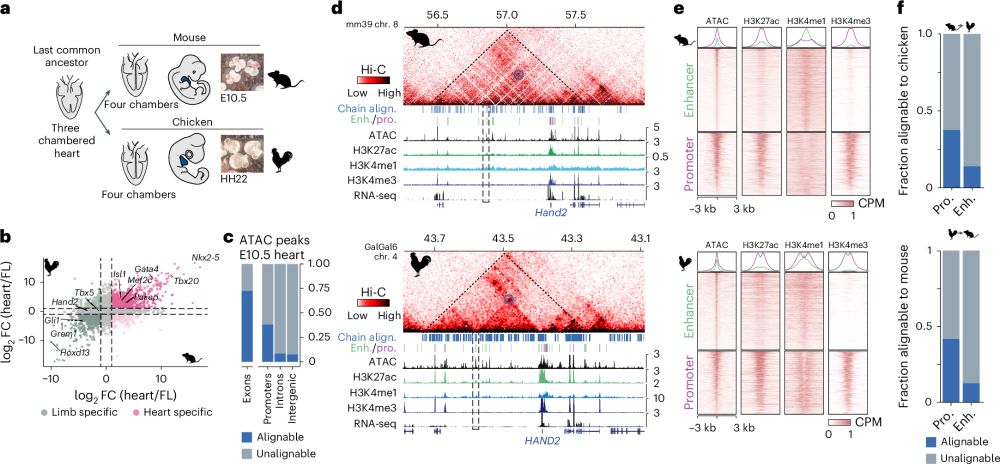
Conservation of regulatory elements with highly diverged sequences across large evolutionary distances
Nature Genetics - Combining functional genomic data from mouse and chicken with a synteny-based strategy identifies positionally conserved cis-regulatory elements in the absence of direct sequence...
How to find Evolutionary Conserved Enhancers in 2025? 🐣-🐭
Check out our paper - fresh off the press!!!
We find widespread functional conservation of enhancers in absence of sequence homology
Including: a bioinformatic tool to map sequence-diverged enhancers!
rdcu.be/enVDN
github.com/tobiaszehnde...
27.05.2025 12:19 — 👍 246 🔁 110 💬 7 📌 9
Thanks!
28.05.2025 13:30 — 👍 0 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
Thanks!
We don't know specifically about the sliding length - but that's definitely something we would like to look at.
And thank you for reminding me about your paper, very relevant and interesting.
28.05.2025 00:17 — 👍 1 🔁 0 💬 0 📌 0
18/
Kudos to Nir Strugo (nirstrugo.bsky.social) who led the work, with help from Carmit Burstein, Noam Nago, and Hadeel Khamis, and also Saddam Hossein from the Hoffman Lab.
Thanks to Hagen Hofmann, Naama Barkai, Moshe Goldsmith, Gabi Rosenblum and vmindel.bsky.social��� for comments and/or help!
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
17/
Bottom line:
Using single-molecule assays, we show that IDRs modulate Msn2 binding to its target motif by tuning genome exploration.
This occurs via non-specific (or rather quasi-specific) association and sequence-sensitive facilitated diffusion, shaped by disordered regions.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

16/
Together, our results support a model in which IDRs:
1. Facilitate initial non-specific association, stabilized by the DBD. Association, stabilization, or both, are sensitive to the sequence.
2. Enhance sequence-dependent diffusion toward the motif.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 1 💬 1 📌 0

15/
What about the diffusion? sequence-sensitive ?
We perturbed IDR function during the sliding phase only (post-binding).
This had no effect for the arb. seq. but reduced STO probability and delayed detection for Hap4
⇒ IDRs enhance diffusion in a sequence-sensitive manner.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

14/
Can we pinpoint which specific phase of the search is sequence-sensitive?
Hap4 showed increased non-specific binding, while dissociation rates (very low for both environments) were similar.
Conclusion: initial association, but not dissociation, is sequence-sensitive.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

13/
Can this mechanism explain Msn2’s promoter selectivity?
We tested by replacing our "arbitrary" flanking region with a segment from the Hap4 promoter (a native Msn2 target).
Strikingly, STO binding increased to ~100%, and TFs were detected faster.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

12/
Surprisingly, TFs were detected at the motif in ~30% of molecules, despite no free TFs in solution and irreversible dissociation conditions. This required intact IDRs, supporting a search mechanism based on non-specific binding and 1D diffusion on DNA.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

11/
To test this, we developed a new assay, which we called Sliding-to-Target Occupation (STO):
We unzip DNA, incubate with TFs for 1 min, and then move to a TF-free channel where we perform repeated unzipping cycles to detect binding at the motif.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
10/
Since IDRs increased both non-specific binding and association to the motif, we asked:
Can these non-specifically bound proteins ultimately reach the motif by sliding on DNA?
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

9/
We also found that Msn2 interacts with single-stranded DNA through its IDRs. This was evident in rezipping hysteresis, EMSA, and the kinetics of DNA hairpin closing.
These interactions may be relevant for binding melted promoter regions during activation.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
8/
Based on these assays, and complementary EMSA and mass photometry experiments, we could conclude that IDRs promote cooperative formation of non-specific multimeric Msn2–DNA complexes, which are further stabilized by the DBD.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 2 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

7/
During unzipping, we also detected non-specific binding events, evident as peaks far from the canonical motif.
These were frequent with full-length Msn2, rare with the DBD alone, and absent with the IDRs only or in protein-free controls.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

6/
So IDRs affect the affinity, but is this due to a change in association or dissociation rate?
With our previously developed fluctuation assay (Khamis 2021), we saw that IDR deletion didn't affect k_{off} but reduced k_{on} 6-fold
⇒IDRs enhance association, not stability.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

5/
Charge-mediated interactions mediate IDRs contribution: Adding free L-arginine reduced binding, but the effect was reversed at pH 9.8, where arginine is neutral. Notably, the DBD-only variant was less affected, giving us a tool to selectively perturb IDRs.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

4/
Removing the IDRs sharply reduced both the probability and strength of binding at the recognition motif.
This suggests that IDRs enhance binding affinity.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0

3/
Msn2 has a canonical zinc finger DNA-binding domain (DBD) flanked by long IDRs.
What role do these IDRs play in DNA binding?
We used a single-molecule DNA unzipping assay capable of detecting DNA-bound proteins, and three variants: WT, DBD-only, and IDR-only.
27.05.2025 22:10 — 👍 3 🔁 0 💬 1 📌 0
Chromatin and Epigenetics Research at the Technion
Musings about science, biophysics, inference, and occasionally Bach and Shostakovich
Epigenetics, transposable elements, plant biology.
Postdoc @ Gregor Mendel Institute (Vienna, Austria).
@gmivienna.bsky.social
Single Molecule Biophysics
Quantum Photonics
We study the physical basis behind how biological systems work at the nanoscale, focusing on the role of force, using single-molecule and nanoscale methods
https://www.wonglab.tch.harvard.edu
News from the Sternberg lab at Columbia University, Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Posts are from lab members and not Samuel Sternberg unless signed SHS. Posts represent personal views only.
Visit us at www.sternberglab.org
Professor at @jku.at | protein mechanics, molecular force sensors, mechanoresponsive materials | #MentorFirst | #FirstGen | 🇩🇪 in 🇦🇹 | www.jku.at/biom
Professor of Biological Physics at Oxford.
Genomics, Machine Learning, Statistics, Big Data and Football (Soccer, GGMU)
PI at EPFL / gene regulation / chromatin / epigenetics / genomics / stem cells / transcription factors / single molecule / protein turnover https://www.epfl.ch/labs/suter-lab/ - and 🎹 https://www.youtube.com/@davidsuter594 / https://soundcloud.com/suterd7
Scientist at University of Edinburgh. Director of MRC Human Genetics Unit but posting in my own capacity.
The Chory Lab @ Duke-- #NewPI developing new therapies & tools to study gene regulation using robotic directed evolution. Tweets by @chorye & lab members
Professor of Computational and Molecular Biophysics at Cambridge University. We work on multiscale modeling of chromatin and biomolecular condensates. From Mexico City 🇲🇽. Mum of two (She/Her)
Genetics professor at Harvard Medical School. Interested in RNA life cycles and genome organization across the cell, from the nucleus to mitochondria.
Cellular Nanoscience Lab at University of Tübingen
Managed by lab members
https://tinyurl.com/CellNano
Molecular endocrinology and epigenetics lab at the Technion
#chromatin #endocrinology #pituitary #reproduction #epigenetics
Associate Professor, Mechanobiology and Single Molecule Biophysics @ LENS & University of Florence, Italy
Physics at Ulm University | live-cell/organism single-molecule microscopy | super-resolution microscopy | gene regulation | chromatin architecture | embryo development
The Marqusee Lab @UCBerkeley uses #biophysics to study #proteinfolding in basic and cellular contexts. Account is student/postdoc run. All posts in kcal/mol.
Molecular Transport in Cell Biology and Nanotechnology - Research group of Stefan Diez at B CUBE, TU Dresden and MPI-CBG Dresden